INFO: The handbook is optimized for environments supporting Mermaid.js diagrams. For static export, rasterized versions are available in Appendix A.
This document maps the AI System Lifecycle to the foundational disciplines defined by the ACM/IEEE Joint Task Force on Computing Curricula (available at https://
The Foundational Computing Disciplines and Their Contribution to Production AI Systems¶
The table below maintains the official ACM/IEEE Computing Curricula structure but reclassifies ACM’s “Data Science” for terminological accuracy in a production context.
| Discipline | Latest Version | Target Audience/Focus Areas | Key Differences/Overlaps | AI/ML Implementation Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computer Engineering | CE2016 | Undergraduate programs in Computer Engineering. | Focuses on hardware-software integration; crucial for specialized accelerator design. | FPGA/ASIC optimization for inference, CUDA kernel development, low-level memory management for HPC. |
| Computer Science | CS2023 | Undergraduate programs in Computer Science. | Broad foundational computing; emphasizes theoretical aspects, algorithms, and complexity. | Algorithm design for efficient sampling, Time/Space complexity analysis of inference, Novel attention mechanism design. |
| Cybersecurity | CSEC2017 | Post-secondary degree programs in Cybersecurity. | Focuses on security competencies; essential for robust, compliant MLOps deployment. | Threat modeling for MLOps pipelines, Adversarial attack mitigation (e.g., poisoning), secure API endpoint deployment. |
| ML/Statistical Foundations[1] | CCDS2021 | Undergraduate programs with a data science focus. | Integrates computing with statistics; focuses on analysis, modeling, and core ML principles. | Feature engineering, Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA), Model selection/hyperparameter tuning, designing evaluation metrics. |
| Information Systems | IS2020 | Undergraduate programs in Information Systems. | Emphasizes business and system competencies; organizational use of information. | Data Governance strategy, Stakeholder management for data access, Explainability (XAI) compliance reporting, Business process modeling around AI outputs. |
| Information Technology | IT2017 | Baccalaureate programs in Information Technology. | Focuses on practical infrastructure and support; vital for monitoring and platform maintenance. (Requires MLOps/SRE augmentation). | Cloud resource provisioning (Terraform/CloudFormation), Containerization (Docker/Podman), System monitoring and alerting. |
| Software Engineering | SE2014 | Specific to the software development lifecycle; emphasizes engineering practices, design, and testing. (Requires MLOps/SRE augmentation). | Microservice design for model serving, Automated testing (unit/load), CI/CD pipeline construction (GitOps), code quality standards. |
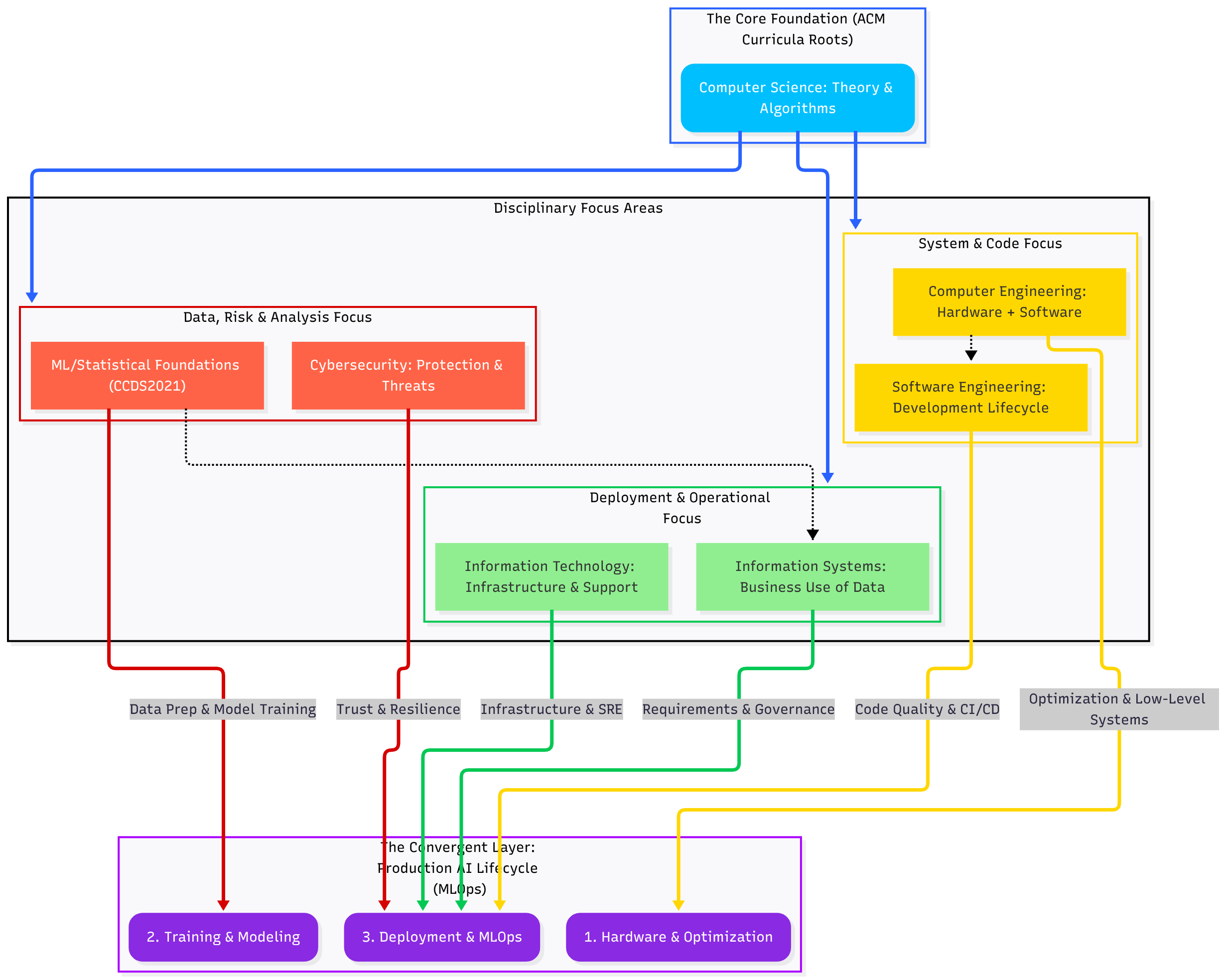
AI Systems Connection to the ACM Disciplines¶
The diagram shows AI Systems not as a separate branch, but as the convergent product of the foundational disciplines.
Breakdown of AI Grounding (Production Context)¶
Hardware & Optimization (AIH)
Grounded in: Computer Engineering (CE2016).
Production Context: Covers high-performance computing clusters and hardware-software co-design. This is where systems thinking and low-level optimization (memory, latency) are applied to specialized accelerators (GPUs, TPUs) for efficiency.
Training & Modeling (AIT)
Grounded in: ML/Statistical Foundations (CCDS2021).
Production Context: The engineering application of these principles is Machine Learning Engineering (MLE), focused on reproducible training, model versioning, bias mitigation, and data pipeline integrity.
Deployment & MLOps (AID)
Grounded in: Software Engineering (SE2014), Information Technology (IT2017), and Cybersecurity (CSEC2017).
Production Context: This phase synthesizes multiple disciplines and must be augmented by MLOps/SRE principles, which go beyond the scope of older curricula. Adherence to standards like ISO/IEC 23053 (AI Engineering Framework) and ISO/IEC 29148 (Requirements Engineering) is mandatory.
Software Engineering handles model integration into scalable, robust microservices.
Information Technology handles the underlying cloud infrastructure, logging, and continuous performance monitoring (the “Ops” of MLOps).
Cybersecurity ensures compliance, integrity, and threat-response, crucial for a trusted service.
Appendix A. Renderred Diagram¶
CCDS2021 provides a competency model for Data Science, not a full degree curriculum equivalent to CS or SE. In a production setting, this discipline is implemented as Machine Learning Engineering (MLE) for efficient deployment.